DETEKSI SERANGAN LOW RATE DDOS PADA JARINGAN TRADISIONAL MENGGUNAKAN MACHINE LEARNING DENGAN ALGORITMA DECISION TREE
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14421/csecurity.2023.6.1.3951Abstract
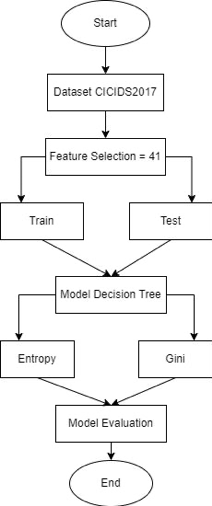
Decision tree adalah salah satu metode yang sering digunakan dalam data mining dan machine learning untuk memprediksi hasil atau mengambil keputusan berdasarkan input yang diberikan. Algoritma ini menciptakan pohon keputusan yang terdiri dari node yang mewakili pertanyaan atau kondisi dan edge yang menghubungkan node-node tersebut. Dalam aplikasinya untuk mendeteksi serangan Low Rate DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) pada jaringan tradisional, decision tree dapat digunakan untuk memprediksi kemungkinan terjadinya serangan Low rate DDoS berdasarkan beberapa fitur yang dianggap penting dalam mengidentifikasi serangan tersebut. Fitur-fitur tersebut bisa berupa jumlah traffic yang masuk ke jaringan, tipe traffic yang masuk, atau karakteristik traffic lainnya. Setelah fitur-fitur tersebut dikumpulkan, Decision tree dapat digunakan untuk memprediksi kemungkinan terjadinya serangan Low rate DDoS pada jaringan tradisional dengan menganalisis fitur-fitur yang dianggap penting dan membuat keputusan berdasarkan pertanyaan-pertanyaan yang sesuai. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menganalisis perbandingan hasil dari dua metode decision tree, yaitu algoritma Gini Index dan Entropy, untuk mendeteksi serangan low rate DDoS (Distributed Denial of Servcice) pada jaringan tradisional dengan menggunakan dataset CICIDS 2017 . Hasil analisis menunjukkan bahwa metode decision tree dengan algoritma Gini Index lebih baik dari Entropy untuk mendeteksi low rate DDoS (Distributed Denial of Servcice) pada jaringan tradisional berdasarkan nilai Accuracy, Precision , dan F1 Score, yaitu dengan nilai 99,740%, 99,113%, dan 99,231%. Namun, metode decision tree dengan algoritma Entropy lebih baik dari Gini Index berdasarkan nilai Recall, yaitu dengan nilai 99,351%.
Kata kunci: Decision tree, DDoS, Machine learning, CICIDS2017, Gini Index , Entropy
---------------------------
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are attacks that can paralyze network traffic and services by overloading servers, network links and network devices (switches, routers, etc.) with very high network traffic. DDoS detection can be done using machine learning, one of which is using the Decision Tree algorithm. Decision Tree is a method that is often used in data mining and machine learning to predict results or make decisions based on the input provided. In its application to detect Low Rate DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks on traditional networks, decision trees can be used to predict the possibility of Low rate DDoS attacks based on several features that are considered important in identifying such attacks. These features can be the amount of traffic that enters the network, the type of traffic that comes in, or other traffic characteristics. To detect low rate DDoS attacks on traditional networks using the CICIDS 2017 dataset. The results of the analysis show that the decision tree method with the Gini Index algorithm is better than Entropy for detecting low rate DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) on traditional networks based on Accuracy, Precision, and F1 Score, with values of 99.740%, 99.113% and 99.231%.
Keywords: Decision tree, DDoS, Machine learning, CICIDS2017, Gini Index , Entropy
References
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Fadil Febriansyah, Zian Asti Dwiyanti, Diash Firdaus

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-SA 4.0)
You are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- ShareAlike — If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.



