Perbandingan Keamanan dan Performa Protokol VMess, VLESS, Trojan, dan WireGuard pada Passwall Berbasis OpenWRT
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14421/csecurity.2025.8.2.5368Abstract
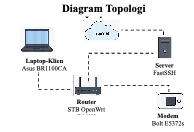
Penelitian ini menganalisis dan membandingkan tingkat keamanan serta kinerja empat protokol tunneling modern: Vmess , Vless , Trojan , dan WireGuard . Implementasi dilakukan menggunakan aplikasi Passwall versi 4.77-6 pada firmware kustom ReyRe WRT berbasis OpenWRT 23.05.4, yang berjalan pada router STB OpenWrt B860H . Penelitian ini menggunakan pendekatan kuantitatif dengan metode eksperimen komparatif untuk memancarkan parameter seperti throughput , latensi , jitter , dan penggunaan CPU . Analisis keamanan dilakukan menggunakan Wireshark untuk mendeteksi enkripsi dan potensi kebocoran data. Hasilnya menunjukkan tidak ada protokol yang unggul di semua aspek. Vless mencatat throughput tertinggi (23.2 Mbit/s), cocok untuk streaming dan transfer data besar. Trojan menunjukkan latensi (110 ms) dan jitter (8 ms) terendah, ideal untuk aplikasi real-time seperti game online dan konferensi video , serta konsumsi CPU paling efisien (1.1%). WireGuard memiliki throughput yang tinggi, namun dengan jitter tidak stabil (hingga 239 ms). Dari sisi keamanan, semua protokol berhasil mengenkripsi payload , tetapi terjadi kebocoran DNS ke router lokal pada konfigurasi default . Oleh karena itu, pemilihan protokol sebaiknya disesuaikan dengan kebutuhan pengguna: Vless untuk kecepatan, Trojan untuk stabilitas, dan Vmess sebagai solusi seimbang.
Kata kunci: tunneling, openWRT, passwall, keamanan, performa, DNS leak
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Comparison Of Security And Performance Of Vmess, Vless, Trojan, And Wireguard Protocols On Opwrt-Based Passwall
This study compares the security and performance of four modern tunneling protocols Vmess, Vless, Trojan, and WireGuard implemented via Passwall version 4.77-6 on ReyRe WRT custom firmware based on OpenWRT 23.05.4, running on a ZTE B860H STB router. A quantitative approach using a comparative experimental method was applied to evaluate throughput, latency, jitter, and CPU usage. Security analysis was conducted using Wireshark to examine encryption effectiveness and detect DNS leaks. The results show that WireGuard achieved the highest throughput (45.2 Mbit/s) and the lowest CPU usage (1.2%), making it ideal for bandwidth-intensive activities. Trojan recorded the lowest latency (7.1 ms) and stable jitter (0.35 ms), making it suitable for real-time applications like VoIP and online gaming. Vmess and Vless performed moderately, with Vmess standing out as a balanced, versatile choice. From a security perspective, all protocols successfully encrypted payloads; however, DNS leaks to the local router were consistently detected under default configurations, posing a significant privacy concern. Statistical analysis confirmed that performance differences between protocols were significant. This study provides data-driven insights for selecting the most appropriate tunneling protocol based on specific user needs and highlights the importance of manual configuration to prevent information leakage.
Keywords: tunneling, openWRT, passwall, security, performance, DNS leak
References
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 fajar; Aulia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-SA 4.0)
You are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- ShareAlike — If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.



